Fizeau Interferometry
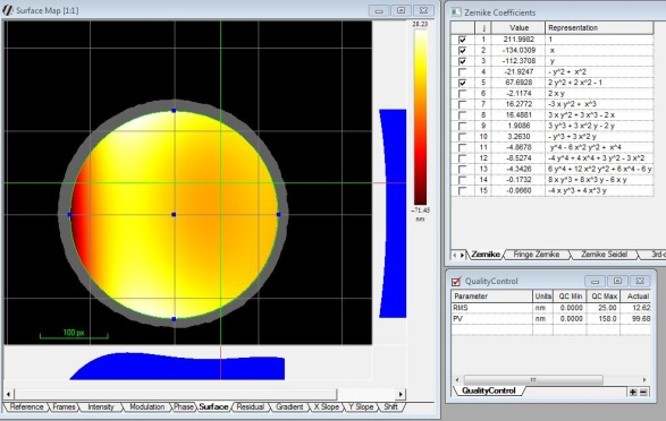
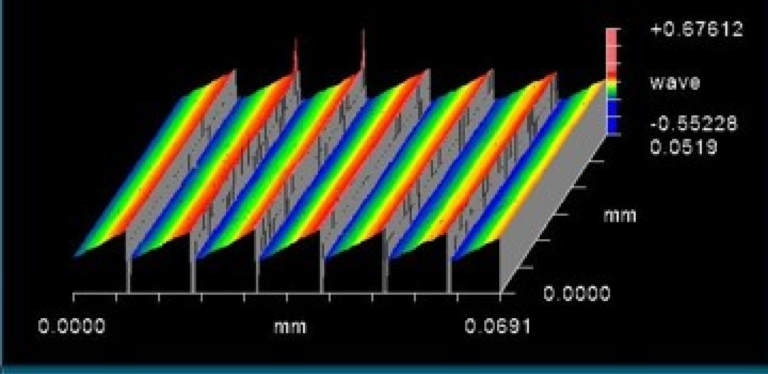
Many characteristics of optical devices are conveniently measured by interferometry. Interferometry is a technique whereby the interference of light is used to measure distances with extreme precision. A Fizeau interferometer is a type of interferometer that is especially suited for measuring the form or figure of optical surfaces. It does this by comparing the surface of the optic-under-test to a master reference surface. The difference in shape between these surfaces can be observed as an interference pattern at the image plane of the interferometer.
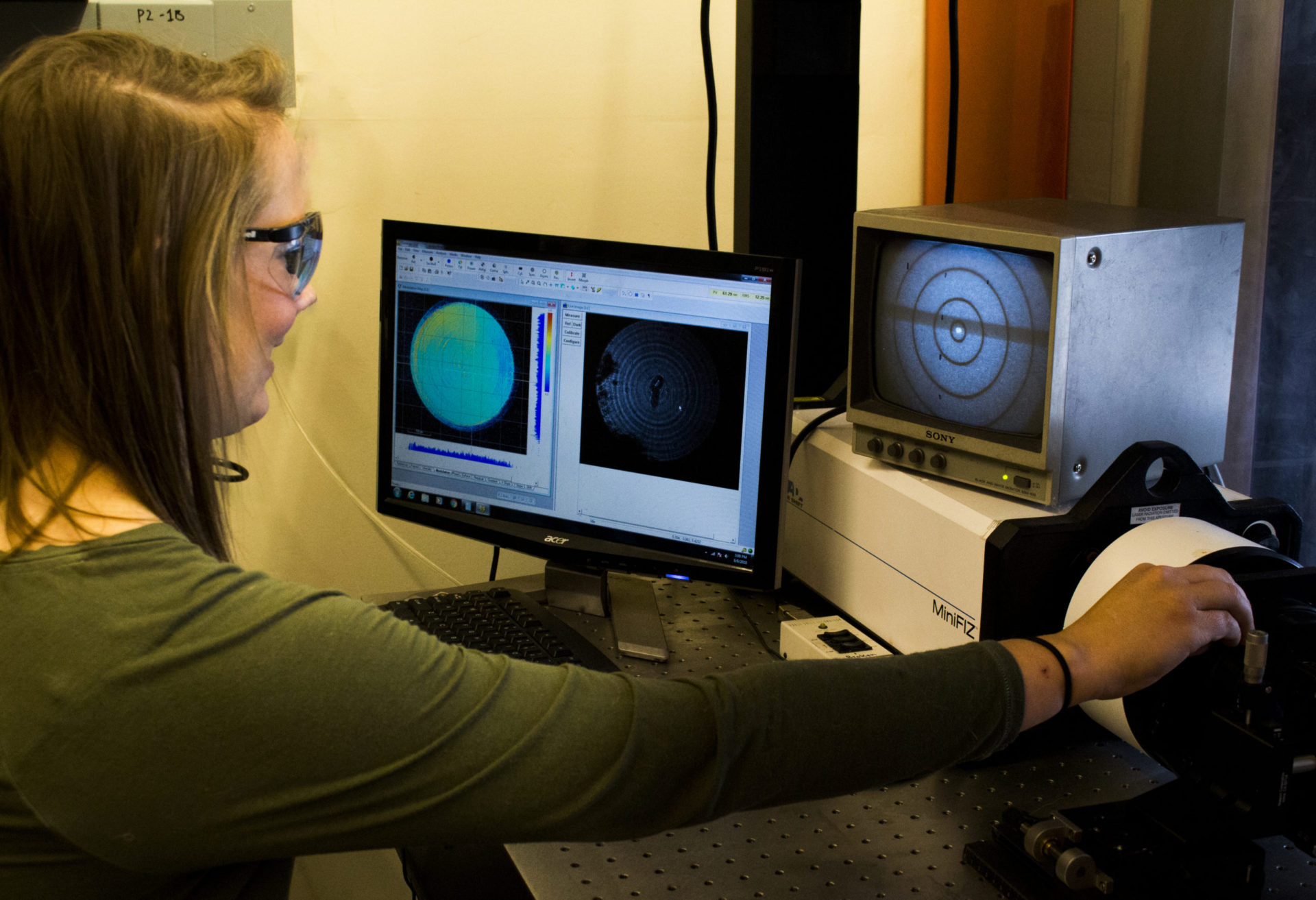
Modern phase- shifting interferometers carefully move the reference optic relative to the optic-under-test and capturing images of the interference pattern with a digital camera. By way of digital image processing one can detect differences spanning many waves of light without ambiguity with extremely high precision. Surface height differences of one one-hundredth of a wave of light can be detected (~6 nanometers).
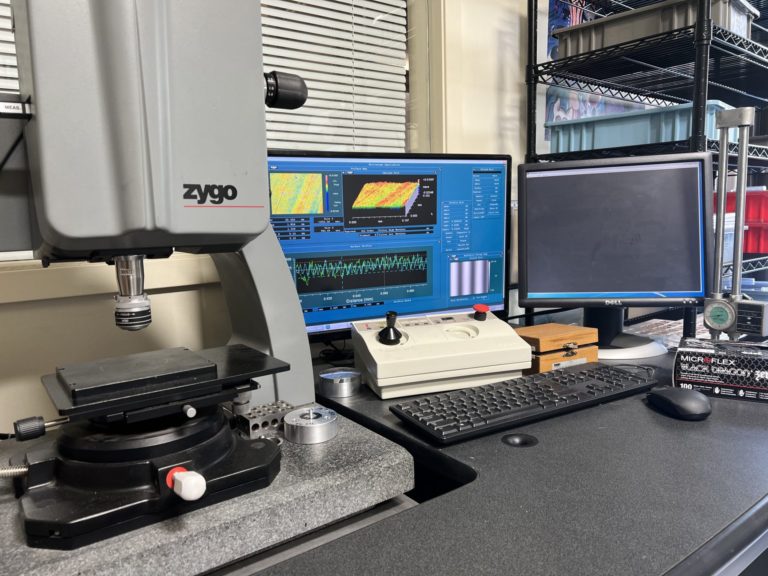
Nanophorm utilizes 6″ Zygo GPI-XP and 4” ADE-MiniFiz Horizontal Phase Shifting Interferometers and a full range of Zygo lambda/10 and lambda/20 transmission reference optics to make a variety of measurements. By comparing to a master reference flat, we can measure the flatness of flat mirrors or plano transmission surfaces, or the wedge of an optical window. If we compare to one of several master transmission spheres, we can measure spherical irregularity or mild aspherical departure. We can extend this technique to measure radius of curvature.